What is a default gateway and why does it matter?

A default gateway is the device on your network that handles any traffic meant to go beyond your local network. In most homes and small offices, it’s the router. When your computer, phone, or smart device needs to reach the internet, it sends that request to the default gateway first, and the gateway decides where that traffic should go next.
In this article we’ll tell you how to find your default gateway on most devices, troubleshoot common issues, give you some security tips, and more.
What is a local network?
A local area network (LAN) is a group of devices connected within a single physical location, where they can communicate with each other without using the public internet. At home or in a small office, this usually means the collection of devices connected to your Wi-Fi or router, such as laptops, phones, smart TVs, and game consoles.
These devices use private IP addresses to talk to each other directly, share files, stream media, or access local services without involving the wider internet.
What does a default gateway do?
The default gateway acts as the exit point for any traffic that needs to leave your local network. When a device wants to reach something outside its own network, like a website or a server on another subnet, it sends that request to the default gateway, which decides where the traffic should go next. Without a default gateway, devices would only be able to communicate with others inside the same local network.
How the default gateway works depends on the environment:
- Home networks: The gateway is usually your router. It takes traffic from your devices and forwards it to the internet, then routes the responses back to the right device.
- Business and enterprise networks: Gateways may be firewalls, Layer 3 switches, or routing appliances. They manage traffic between multiple subnets, apply access rules, protect sensitive systems, and direct traffic toward remote sites or the internet.
- Cloud environments: Gateways are virtual components managed by the cloud provider. They route traffic between subnets, virtual machines, and the public internet and offer built-in high availability and scalability.
What is a default gateway address?
For a device to reach the default gateway, it needs an IP address to identify where that gateway lives on the local network. That internal IP address is the default gateway address, and it’s usually assigned to your router and shared with devices automatically through Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
Most home networks use familiar private IP addresses such as 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, depending on the router model and configuration. Your device stores this address in its network settings so it always knows where to send nonlocal traffic. When you type the gateway address into a browser, you usually reach your router’s administrative interface, where you can adjust settings like your Wi-Fi password, Domain Name System (DNS) server, or network name.
How to find your default gateway address on any device
You can check your default gateway on any operating system, and the process only takes a few seconds. Every device stores this value in its network settings so it knows where to send traffic that leaves the local network.
How to find your default gateway address on Windows
You can find the default gateways through the Command Prompt or Control Panel. Here are the steps for each.
Command Prompt
- Press the Windows icon and the R button to open the Run dialog box. Type cmd and click OK.
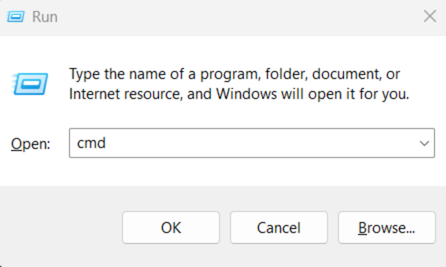
- Type ipconfig in the dialog box and press Enter.
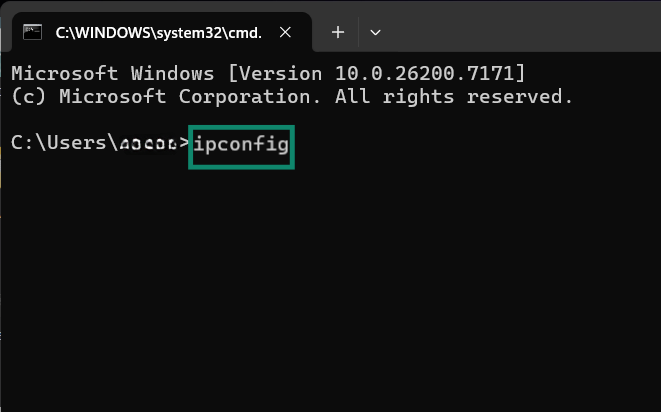
- Your default gateway will appear in the bottom line.
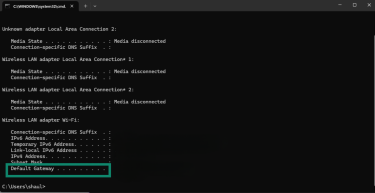
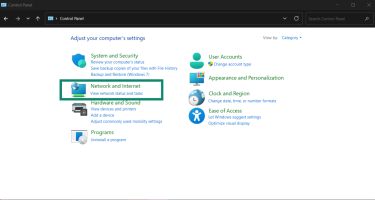
Control Panel
- In the Control Panel, click on View network status and tasks.
- Click on the network listed next to Connections.
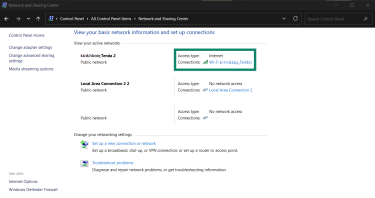
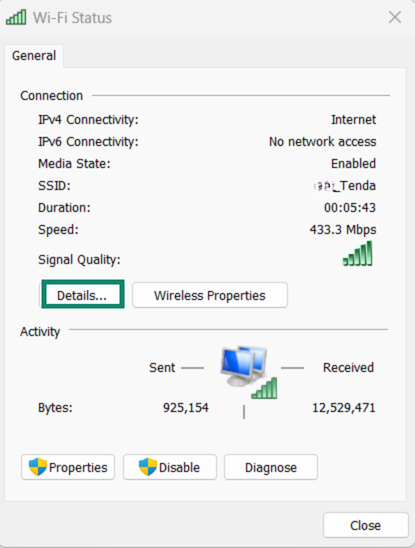
- A dialog box will open. Click the Details button.
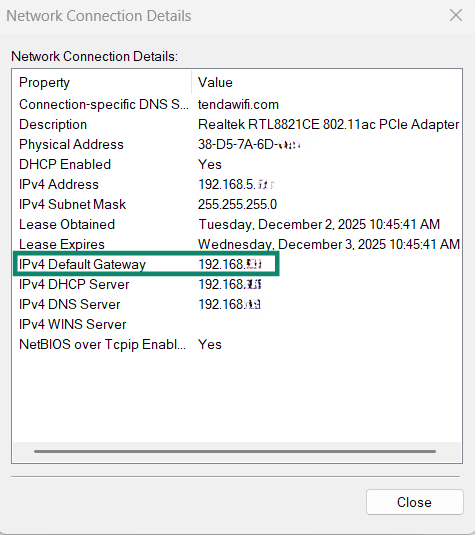
- You’ll see the default gateway next to IPv4 Default Gateway, along with other network connection details.
How to find your default gateway address on macOS
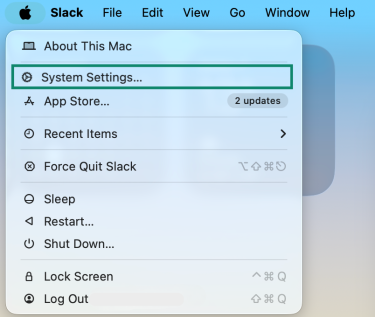
- Open the Apple menu and click on System Settings.
- Select Network.
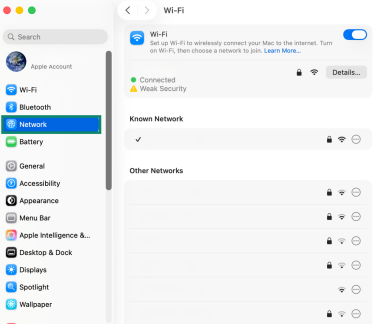
- Next to your active connection, click Details.
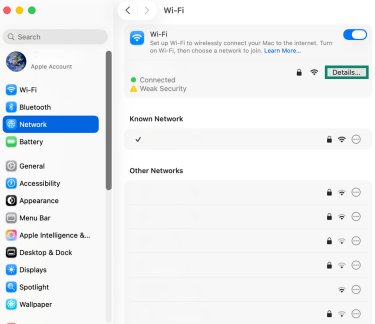
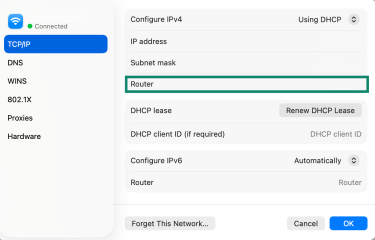
- Select TCP/IP and the default gateway will display next to Router.
How to find your default gateway address on Android
- Open the Settings menu and tap Wi-Fi.
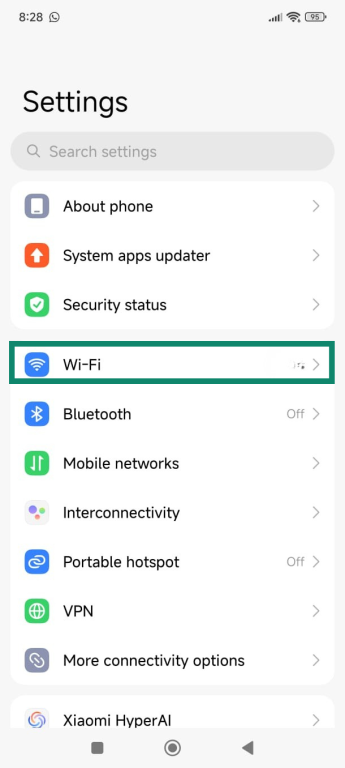
- Tap on the arrow icon next to your Wi-Fi network’s name.
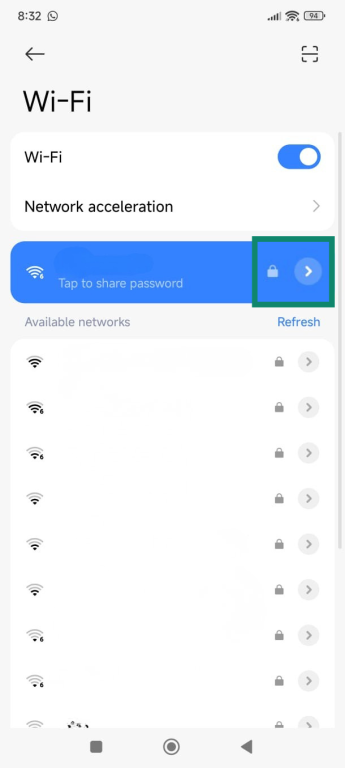
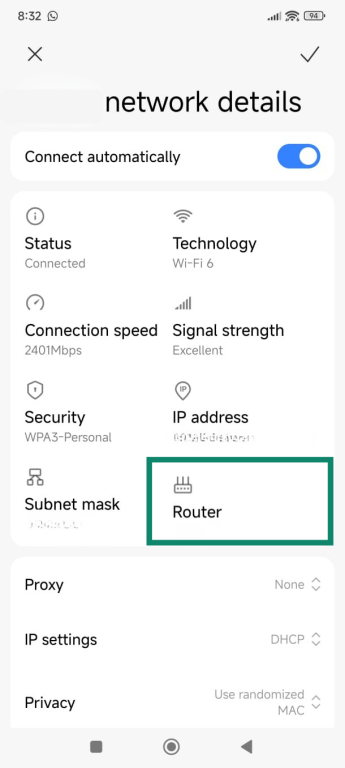
- The default gateway is listed under Router.
Note: The menu options on Android may change based on your device and version number. If you can’t find the menu option listed above, you can also type “Wi-Fi” in the settings search bar to jump directly to the reset option.
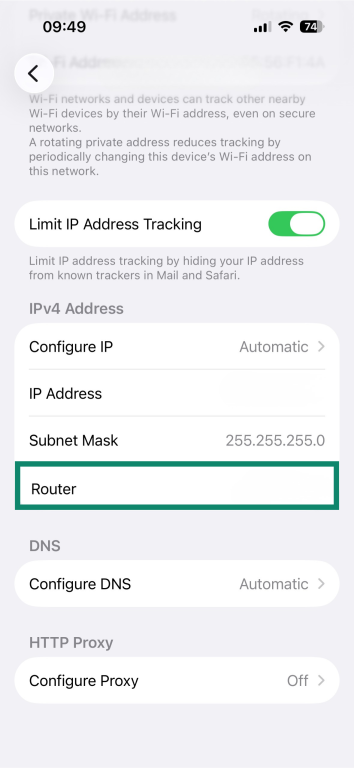
How to find your default gateway address on iOS and iPadOS
- Open the Settings menu on your device and select Wi-Fi.
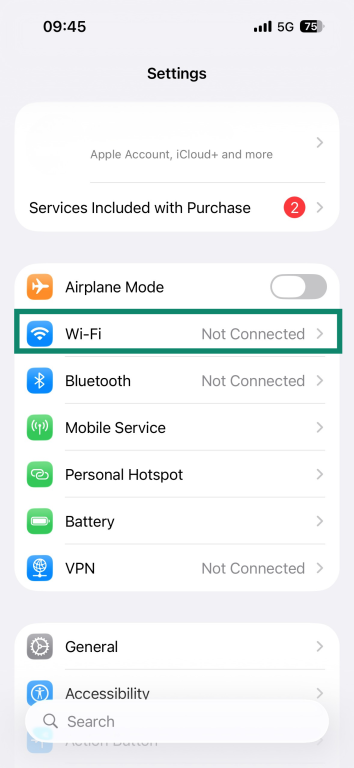
- Tap the info (i) icon next to the network name.
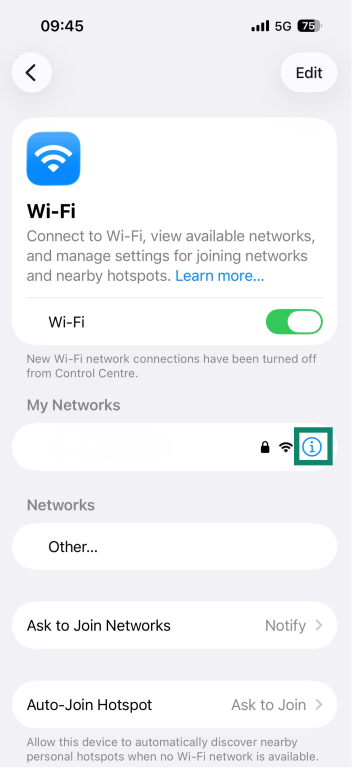
- The default gateway will appear next to Router.
How to find your default gateway address on Linux
- From the app menu, open the Terminal.

- Type ip route.
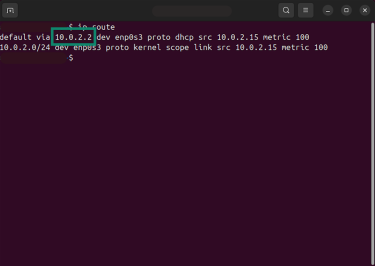
- Find the line that starts with default via. The numbers next to it are your default gateway address.
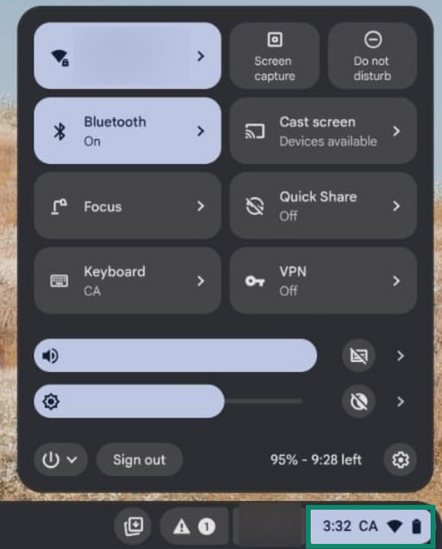
How to find your default gateway address on Chromebook
- Click the Status area on the bottom right corner of your screen where the time and Wi-Fi logo appear.
- Click the Settings (gear icon) option.
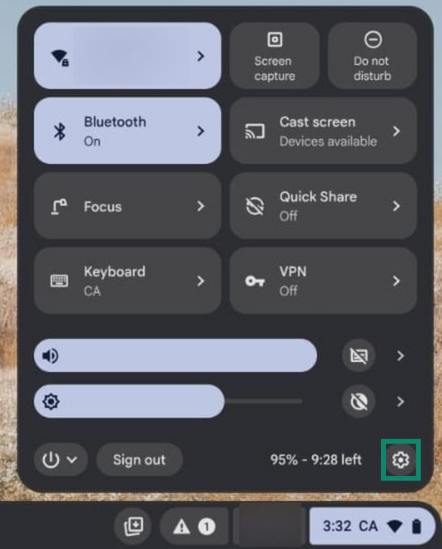
- Select the arrow icon next to your Wi-Fi network connection name and select your Wi-Fi network.
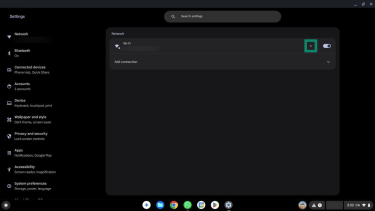
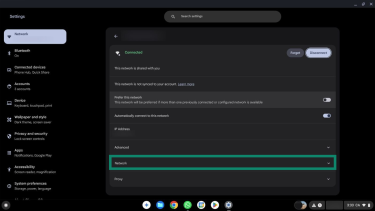
- Go to Network.
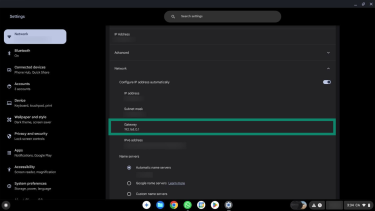
- The default gateway address is listed next to Gateway.
Troubleshooting default gateway issues
Default gateway issues usually look the same from the user’s perspective: the device is connected to Wi-Fi or Ethernet, but nothing on the internet loads. This may manifest as pages timing out, apps being unable to reach their servers, and speed tests not being able to start. Often local resources, like your router’s settings page or a shared printer, still work, which makes the problem confusing.
Most common default gateway errors (and what they mean)
Default gateway problems usually appear in two situations:
- Your device doesn’t have a default gateway configured: Your device doesn’t know where to send traffic beyond the local network.
- Your device has a gateway address but can’t communicate with it: Something on the local network is blocking or breaking that connection.
What does “no default gateway available” mean?
This means your device doesn’t know the default gateway IP address that it needs to reach external networks. This can happen when:
- Your router fails to assign network settings through DHCP.
- Your device may be using incorrect or outdated network configuration files.
- DNS server issues can interrupt lookups and disrupt connectivity.
- Network manager or firewall settings may be blocking traffic by mistake.
The wording for this error varies across systems: Windows often reports this as “The default gateway is not available,” macOS may show a status like “No router found,” and Linux tools typically indicate that no default route exists.
How to fix default gateway connectivity problems
Default gateway problems are generally pretty easy to fix. You want to confirm your device has the correct network settings, check for conflicts on your router, and make sure the software that manages your connection is up to date.
How to reset your network settings safely
Resetting your network settings clears out broken configurations and forces your device to request fresh network details from the router. It’s often an effective fix when your device can’t reach the default gateway because something in the current settings is corrupted.
Note that the reset will erase all saved Wi-Fi networks, custom DNS entries, virtual private network (VPN) profiles, and any manual network settings. Make sure you remember your Wi-Fi password and pause any VPN or security apps so the reset completes cleanly.
Note for Chromebook users: Chromebooks don’t have a single “reset network settings” button, but you can reset everything by clearing saved networks and resetting Wi-Fi components.
How to reset network settings on Windows 11
- Open Settings and go to Network & internet.
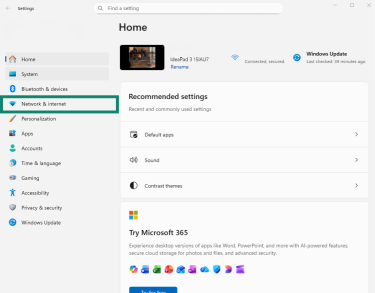
- Open Advanced network settings.
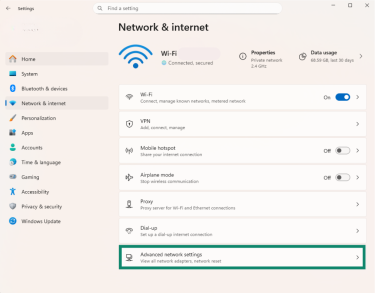
- Choose Network reset.
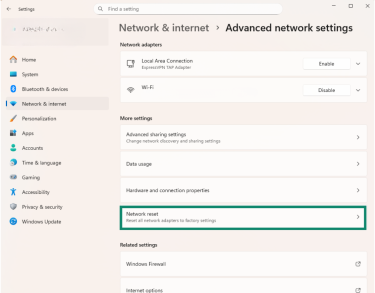
- Click Reset now.
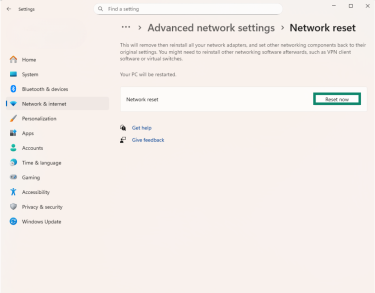
- Restart your PC.
How to reset network settings on Android
- From the Settings menu, tap More connectivity options.
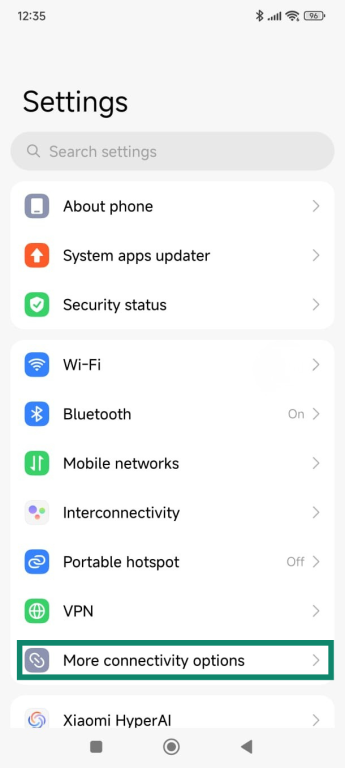
- Scroll down and tap Reset Wi-Fi, mobile networks, and Bluetooth.
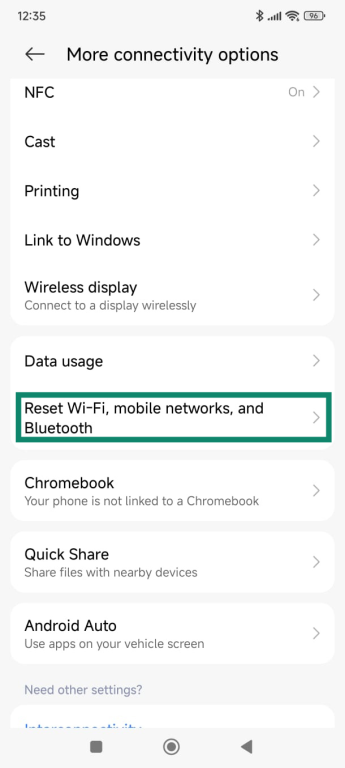
- Tap Reset settings.
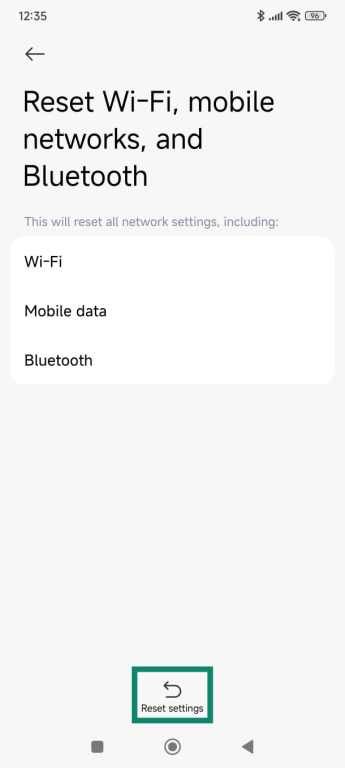
- You may need to confirm with your lock screen pattern, PIN, or biometrics. Then, just restart your Android device.
Note: The menu option on Android may change based on your device and version number. If you can’t find the menu option listed below, you can also type “Reset Wi-Fi” in the settings search bar to jump directly to the reset option.
How to reset network settings on macOS
- In System Settings, select Network in the sidebar, then click the Details button next to your active connection.
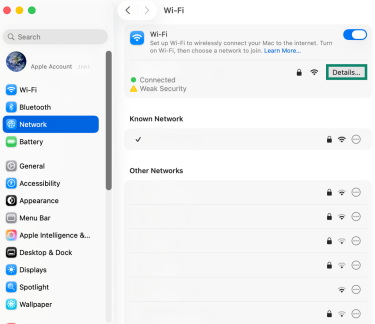
- Scroll down and select Forget This Network.
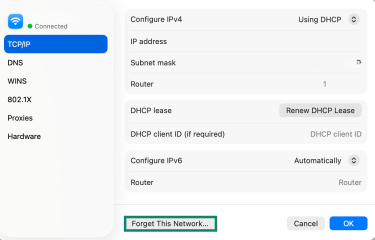
- Click the Network tab again, and then select the network you want to rejoin and click Connect.
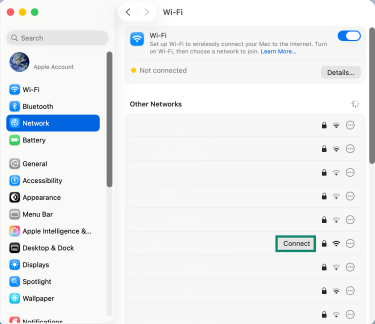
- Restart your Mac.
How to reset network settings on iOS and iPadOS (iOS 15 and above)
- Open Settings and tap General.
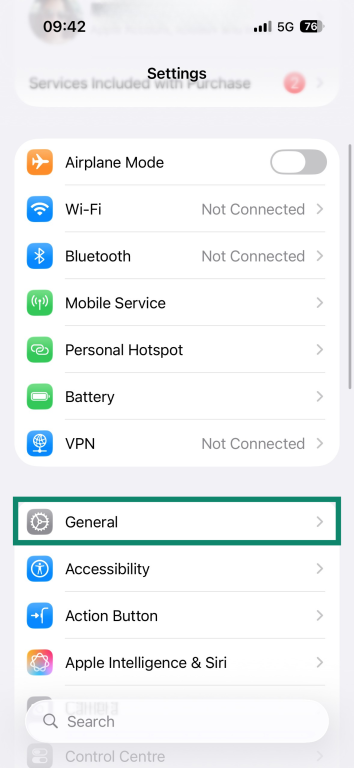
- Scroll down to Transfer or Reset iPhone or Transfer or Reset iPad.
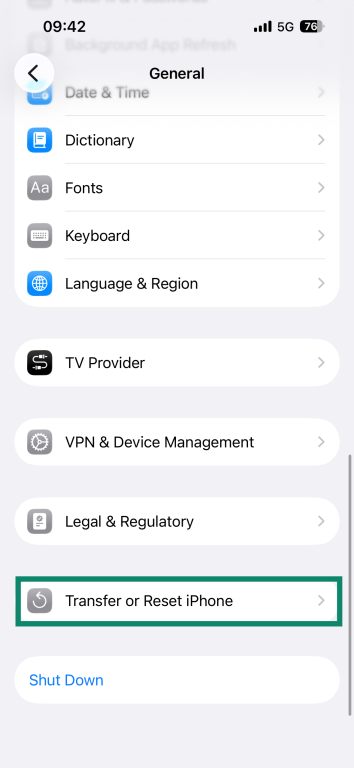
- Tap Reset.
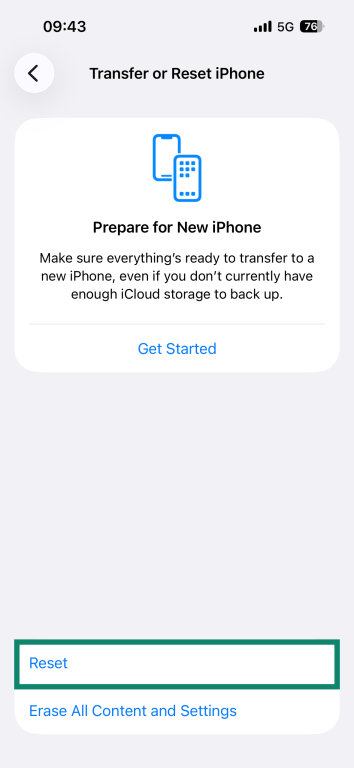
- Select Reset Network Settings.
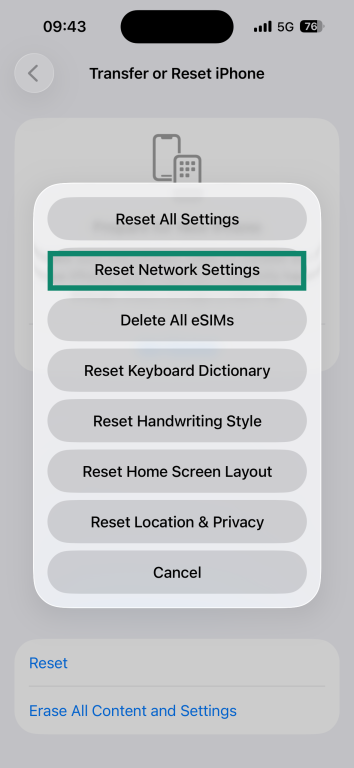
- Enter your passcode.
- Your device will restart automatically.
How to update drivers or router firmware without breaking it
Driver and firmware updates fix bugs, improve stability, and patch known issues that affect network performance. Updating these components can resolve gateway problems, but you want to approach the process carefully to avoid interruptions.
Note for macOS users: Apple automatically updates network drivers on macOS as part of regular OS updates, so there’s no need for manual updates.
Here’s how to manually update drivers on Windows 11:
- Press Windows + X and choose Device Manager.
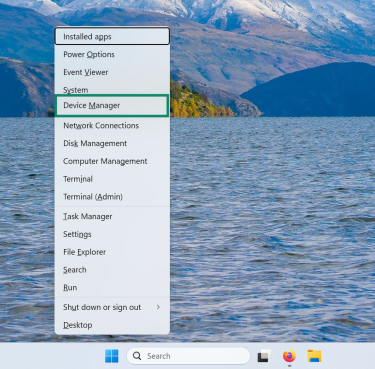
- Expand the Network adapters section and locate your adapters.
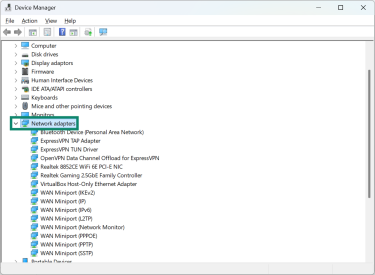
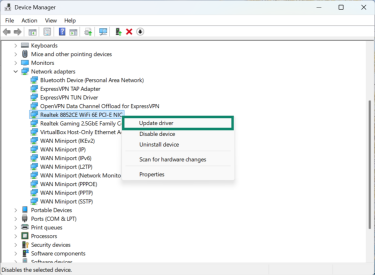
- Select a driver and right-click it with your mouse. Choose Update driver.
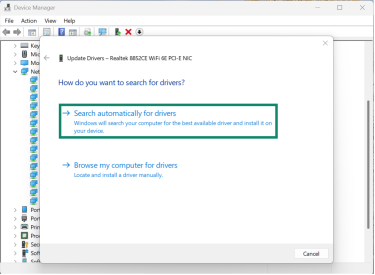
- Click Search automatically for drivers, and Windows will install the update from Microsoft’s database.
- Follow the on-screen instructions and restart your PC when it’s complete.
Driver and firmware update best practices
When updating your network drivers, make sure to follow these best practices:
- Download drivers only from the official support page for your device.
- Install one update at a time so you can track changes.
- Restart your computer after each update.
- Avoid beta drivers unless you are troubleshooting specific issues.
Router firmware updates follow a similar approach:
- Check your router manufacturer’s website for the official firmware version that matches your exact model.
- Create a backup of your router configuration before you update.
- Connect your computer to the router with an Ethernet cable so the update does not fail mid-process.
- Let the router complete the update without interrupting power.
A clean update often resolves gateway timeouts, routing failures, and other issues that block communication between your device and the wider internet.
Security tips for your default gateway
Just like the default gateway guides your devices out to the internet, it also controls who can reach your network from the outside. If someone gains access to your router through weak settings or exposed credentials, they can change configuration details, interfere with your connection, or affect traffic on the local network.
A few simple steps strengthen your router security and reduce the chances of unauthorized access. These practices help protect both home users and small businesses that rely on stable and private connections.
Change default login credentials
Routers, firewalls, and other gateway devices often ship with default usernames and passwords that are publicly documented. If you don’t change them, anyone who joins your network or gets close enough to connect can potentially log in and take control of your gateway. A reliable password manager can help you create a strong, unique password and store it safely so you don’t lose access.
Keep the gateway’s software or firmware updated
Outdated firmware often contains known security flaws that attackers actively search for. Updating the software patches those weaknesses and prevents someone from using old exploits to crash the gateway or redirect your traffic.
Disable remote management unless you need it
Remote management lets you access the gateway’s settings from outside your network. If you don’t use this feature, leaving it enabled only gives attackers another way to reach your device. Turning it off ensures the admin panel stays accessible only from inside your own network.
Control who can reach the gateway
The fewer devices that can access the gateway’s admin page, the safer it is. Strong Wi-Fi security at home or proper network segmentation in business networks prevents unknown or untrusted devices from even reaching the gateway interface.
Avoid unnecessary open ports
Features like Universal Plug and Play (UPnP), broad port forwarding, and demilitarized zone (DMZ) create openings that attackers can scan for. If you don’t explicitly need them, turn them off. Closing unused ports keeps the gateway focused on routing traffic instead of exposing extra services.
Separate untrusted devices
Smart home gadgets, visitors’ devices, and low-security hardware can be compromised more easily than your primary devices. Putting them on a guest network or separate virtual local area network (VLAN) keeps them isolated so they can’t reach the gateway’s management interface or interfere with your main network.
FAQ: Common questions about default gateways
Is 192.168.1.1 a default gateway?
Many home routers use 192.168.1.1 as the default gateway. This address sits inside the private IP range reserved for local networks. You can type it in the address bar on your browser to log into your router and access the admin panel.
What does a default gateway of 0.0.0.0 mean?
A default gateway of 0.0.0.0 means your device does not have a valid gateway assigned. This value usually appears when the router fails to give your device proper network settings through the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or when the device can't reach the router during startup. Without a valid gateway, your device can’t connect to the internet.
Is 192.168.0.1 a default gateway?
Many routers use 192.168.0.1 as the default gateway address instead of 192.168.1.1. Manufacturers choose different defaults, but both addresses are common in home networks. If your device lists 192.168.0.1 as its gateway, it means your router uses that value for routing local traffic to the internet.
How do I fix my default gateway?
You can fix default gateway issues by checking your router, refreshing your device’s network settings, and updating your drivers. Restart your router first, then reconnect your device to the network. If the issue persists, check the gateway value in your network settings to confirm it matches your router’s IP address. Updating router firmware or network drivers can also help when the gateway does not respond or fails to route traffic correctly.
What are common default gateway addresses?
Common default gateway addresses include:
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.1.254
- 10.0.0.1
- 10.0.1.1
Routers from different manufacturers use different defaults, but they all belong to private IP ranges reserved for local networks. You can view your gateway value in the network settings on your device.
How can I change my default gateway?
You can change your default gateway through your router’s administrative interface. Log in using a browser, go to the local area network (LAN) or network settings section, and update the router’s local IP address. Your router will then assign new gateway information to devices through the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
Why is my default gateway not responding?
When your default gateway doesn’t respond, your device reaches the gateway address but doesn’t receive a reply. This can happen when the router freezes, becomes overloaded, or experiences interference on Wi-Fi. Outdated network drivers or an IP conflict on your local network can also cause this.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN