Is BlueStacks safe? Complete guide
Numerous Reddit threads and online forums raise concerns about BlueStacks. Some users claim the installer contains malware, others mention bloatware or system slowdowns, and some report that their antivirus flagged the program as potentially unsafe. In response, BlueStacks frequently states on social media that its software is completely safe.
So what’s the truth behind these claims? In this article, we’ll take a closer look at BlueStacks and explain how it works, the risks and benefits, and how to stay safe if you choose to use it. After reading, you’ll be able to make an informed decision about whether to download BlueStacks or to find an alternative.
What is BlueStacks, and how does it work?
BlueStacks is an Android emulator for Windows and macOS. It lets you run mobile apps on your computer by creating a virtual Android environment that behaves like a separate device. The company is based in the U.S., and it has received support from major tech and hardware companies, including a documented partnership with the U.S.-based semiconductor manufacturer AMD.
Instead of running directly on your hardware like a typical PC or Mac program, BlueStacks operates as a virtual Android system within a window. Inside this environment, it can install and run Android apps and handle Android-specific file formats such as Android Package Kits (APKs), which are functions that Windows and macOS don’t natively support outside of an emulator. The apps themselves run inside this virtual environment while using your computer’s processor, graphics card, memory, and storage.
This setup lets you play mobile games, run Android utilities, and test apps on a desktop system without needing a physical Android phone.
Is BlueStacks safe to use?
When people ask this question, they usually have one or more of the following concerns:
- Is it free of malware or hidden software?
- Will it slow down or damage my computer?
- Does it protect my privacy and account data?
- Does it install third-party software I don’t want?
- Is it stable and reliable over time?
These are all valid concerns, and we’ll answer them all to give a clear picture of how BlueStacks behaves on both Windows and macOS.
Safety for Windows and Mac users
When downloaded directly from the official website, BlueStacks is generally considered safe for use on Windows and macOS. It doesn’t come bundled with malware or spyware when obtained from the official source, and antivirus alerts are typically false positives related to how emulators work.
The key factor is the installation source. The official installer is safe, but modified or repackaged versions from third-party websites should be avoided. Likewise, installing untrusted or pirated Android apps inside BlueStacks carries the same risks as installing them on any Android phone.
We downloaded the latest version of BlueStacks 5 and uploaded it to VirusTotal, a service that checks files against dozens of antivirus engines. None of the 63 antivirus programs that scanned the file flagged it as being malicious.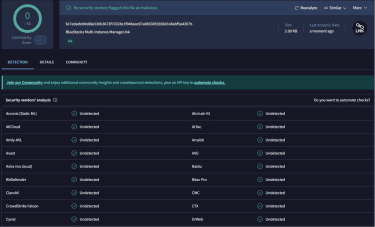
It’s important to note that while the official installer is safe, malware risks can arise if you install third-party APKs inside BlueStacks or download modified versions from unofficial sources. Always exercise the same caution you would on a real Android device.
Is your Google account safe on BlueStacks?
Signing into a Google account inside BlueStacks is generally safe. In fact, you need a Google account to activate BlueStacks so you can download apps from the Play Store.
Some users have complained that when they log in, they get a Google Critical Alert that a new device login was detected on a different device. This is normal behavior, as Google recognizes BlueStacks as a virtual Android device that doesn’t match your usual device fingerprints.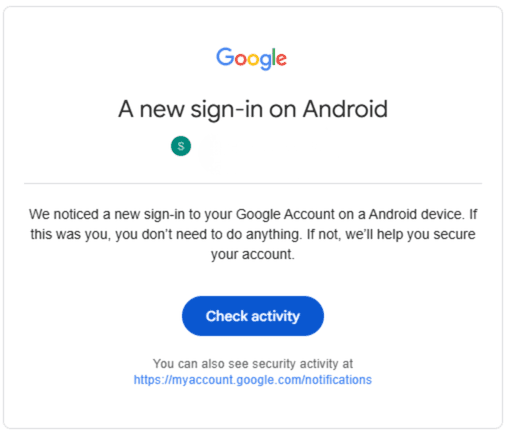
When you click the Check activity button, Google shows details about the login, such as the device model, location, and IP address. In our testing, the alert appeared even though the account was not accessed on any other physical device, confirming that the warning comes from the emulator’s virtual device profile. These alerts are not signs of account compromise.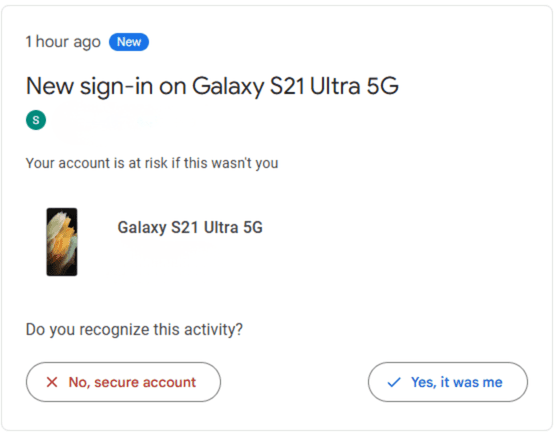
When you log into your Google account, some information (called “third-party account info” in the company’s privacy policy) from that account may be transmitted to BlueStacks, but the company does not specify which data fields are collected. That’s why it’s advisable to create a secondary Google account just for BlueStacks. Just keep in mind that it won’t sync your app activity with your regular account.
Can BlueStacks access files or the microphone?
BlueStacks doesn’t automatically access files from your computer, but you can upload files from your PC or Mac to BlueStacks' Media Manager. It’s a simple drag-and-drop function, and it makes the file accessible within the emulator. This process requires explicit user action; BlueStacks can’t read arbitrary files on your system without your consent.
BlueStacks also provides microphone access to apps running inside the emulator. You can choose which microphone to use in the device settings. While BlueStacks doesn’t restrict the microphone by default, it relies on Android’s permission system to control which apps can access it.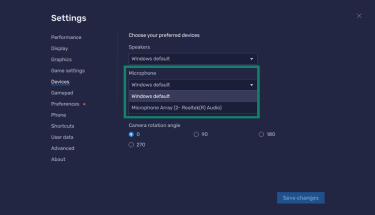
When you install an app, it may request access to the microphone (or other hardware). You can grant or deny these permissions straight away or change them later in the app settings within BlueStacks. This works the same as on a physical Android device: the emulator enforces app-level permissions rather than giving unrestricted access to all software running on your computer.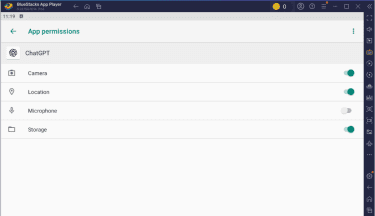
Performance and system impact
Many users assume that because BlueStacks can be CPU or RAM-intensive, it must be too heavy for their system. In most cases, it runs smoothly if your device meets the minimum requirements, but performance depends on your system’s resources and how many apps are running simultaneously.
Does BlueStacks slow down your PC?
BlueStacks can cause slowdowns if your system is already under heavy load or has limited available memory. This isn’t a sign that the emulator is unsafe; it happens with most applications that need to share the computer's resources, and it simply reflects the combined demand to run multiple applications at once.
There are performance controls, such as Eco Mode, frame rate limits, and CPU or RAM allocation options that can help improve your computer’s performance. Adjusting these options can reduce strain on your system and improve responsiveness while the emulator is active.
To open Eco Mode, click on the performance icon on the right-side menu bar. Once activated, you can turn the sound on or off and select the FPS you prefer.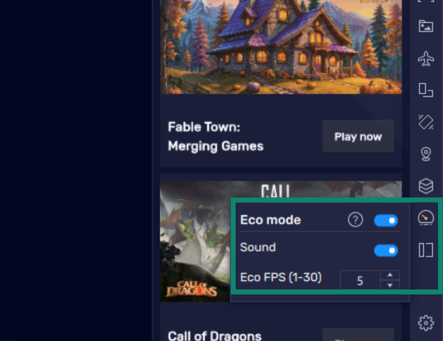
To adjust the other performance settings, follow these steps.
- Click on the Settings gear on the right-hand menu.
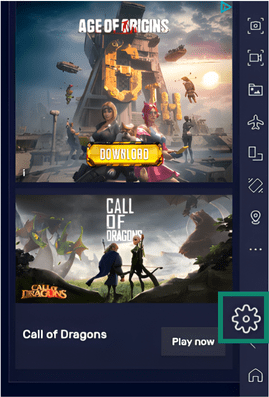
- This opens the Performance page. You can adjust the CPU and Memory allocation, Performance mode, and Frame rate. When you’re done, press the Save changes button.
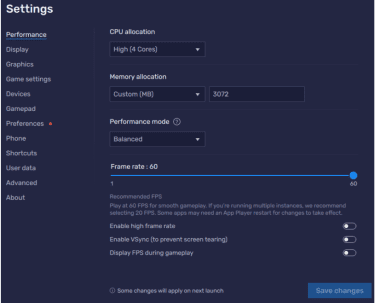
You can adjust these settings until you find the right fix for your specific device.
Performance on low-end vs. high-end devices
BlueStacks works on low-end devices as long as they meet the minimum requirements, although you may need to adjust performance settings for smoother results. Common adjustments include:
- Reducing the emulator’s display resolution and pixel density to decrease GPU load.
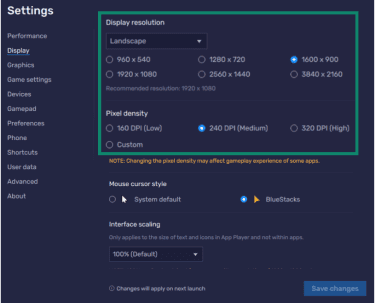
- Switching the interface renderer from Auto to Software, OpenGL, or DirectX if it’s more compatible with your hardware.
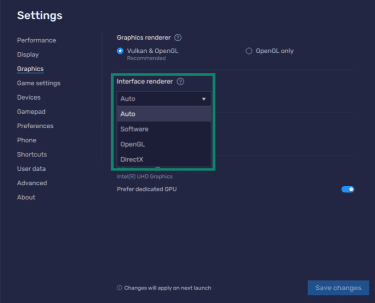
Users can also make some Windows optimizations, such as closing background applications or updating graphics drivers from the manufacturer’s official website. These steps improve overall system stability and can help BlueStacks run more smoothly.
High-end systems typically have enough CPU, RAM, and GPU capacity to run BlueStacks with minimal impact on other tasks. For these devices, performance tuning is usually optional rather than necessary.
Note: Even with adjustments, running multiple high-demand apps simultaneously can affect performance. Eco Mode and CPU/RAM allocation are helpful tools, but they can’t completely eliminate the load caused by resource-intensive apps.
Privacy and data collection
According to its privacy policy, BlueStacks collects information you provide directly, such as your email address, account details, and (in cases like promotions) your name, address, phone number, and photo. If you sign in through a third-party service (e.g., Google, Facebook, Twitch), BlueStacks receives some information from that account, though it doesn’t specify exactly what data is included.
The platform also gathers extensive device and usage data automatically. This includes device identifiers, IP addresses, crash logs, app activity (installations, launches, failures, and network activity), system configuration, metadata about your Android apps, purchase history, and cookie-based browsing behavior. Location-enabled apps can provide anonymized geolocation data if you grant permission.
BlueStacks uses cookies and allows third-party advertisers and analytics partners (notably Google Analytics) to collect certain non-identifying usage data. “Do Not Track” signals from your browser are not honored.
BlueStacks doesn’t sell personally identifiable information but does share data in specific situations, such as with service providers, affiliated businesses, analytics partners, and advertisers (in aggregate or anonymized form). Personal data may also be disclosed to comply with legal requests or transferred during mergers, acquisitions, or other business changes.
Does BlueStacks share or sell my info?
BlueStacks claims that it doesn’t sell personally identifiable information to anyone. It may, however, share general, non-personal usage information with its partners so they can understand how people use the software and improve their services. This data is typically aggregated or anonymized, rather than tied to individual users.
It’s important to note that while BlueStacks doesn’t sell personal data, information transmitted through third-party apps within the emulator may be subject to those apps’ privacy policies, so you need to be aware that app-level data collection is separate from BlueStacks’ own policies.
How long does BlueStacks store user data?
BlueStacks doesn’t state in its privacy policy how long it keeps data. It only lets you access, update, or delete basic account details, namely, your nickname, avatar, and email, through your account settings.
California residents can request details about what personal information is shared for marketing purposes, and EU residents have additional rights under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
You can request deletion of your personal data by email, providing enough information for BlueStacks to reliably verify your identity, and describe your request in sufficient detail. BlueStack will aim to respond to your email within 30 days.
How to stay safe while using BlueStacks
As we’ve discussed, as long as you download the official BlueStacks app and keep it updated to the latest version, the platform is pretty safe. However, the emulator behaves like an Android device, so the same safety habits you use on a phone should also apply here. These steps help reduce risk and keep your information protected.
Use antivirus and anti-malware tools
Security software can help detect harmful files, especially if you’re installing apps from a third-party APK store (which we don’t recommend). Antivirus alerts about BlueStacks itself are usually false positives, but genuine threats can appear through unsafe APKs or modified installers. Keeping your security tools active adds an extra layer of protection.
Secure your Google account
Avoid signing in with a primary Google account if you prefer to reduce account-linked activity. If you do sign in with your main Google account, treat the emulator as you would a new Android device. Enable two-step verification and review sign-in alerts. Note that the email notifications that mention a different Android version are normal for emulators, not signs of account compromise.
Avoid risky APK sources
One of the biggest safety risks comes from downloading APK files from unofficial or unverified sources. Modified APKs can contain malware, adware, or hidden code that compromises your system. Stick to the Google Play Store or reputable developers whenever possible.
Keep your software updated
Enable automatic updates for BlueStacks, your OS, and your graphics drivers. Updates include stability improvements and security patches that help protect the emulator and your computer from known vulnerabilities. Also, older versions of BlueStacks can perform poorly or cause compatibility issues, which is another reason to stay updated.
Take care with app permissions
Apps inside BlueStacks request permissions, just as they would on a phone. Review these requests carefully, and only allow access to the microphone, camera, or shared folders when the app truly needs them.
Use a virtual private network (VPN)
A VPN for mobile gaming can help protect your internet connection while using BlueStacks by encrypting your traffic and masking your IP address from the apps and game servers you use. Since BlueStacks relies on your computer’s network, a VPN on your Windows or macOS device automatically covers the traffic coming from apps inside the emulator as well.
Keep in mind that a VPN only protects your data in transit. It hides your online activity from local network administrators and prevents your internet service provider (ISP) from seeing which apps or services you’re accessing, but it does not hide your IP address from your ISP (they will still see that you’re using a VPN and the amount of data being transmitted), and it does not stop BlueStacks or individual apps from collecting account information, device identifiers, or other telemetry. Review the privacy practices of both BlueStacks and the apps you use in BlueStacks to understand what data they collect beyond your network traffic.
How to uninstall BlueStacks safely
Windows
You can uninstall BlueStacks from your PC in a few easy steps:
- Start typing Add or remove programs in the Windows search bar and click on the option when it appears in the Start Menu.
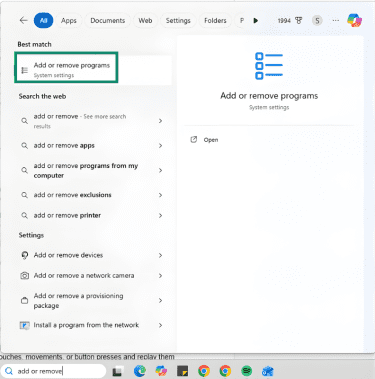
- Find BlueStacks in the list of installed programs. There should be multiple BlueStacks files; click on the three dots next to the largest file, and select Uninstall.
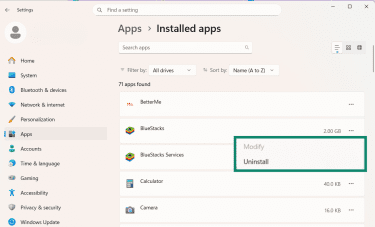
- Confirm that you want to delete this BlueStack file and its related info by clicking Uninstall again.
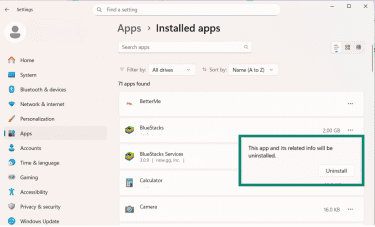
- A pop-up window from BlueStacks will open asking why you’re deleting. You can provide a reason or just click the Uninstall button.
- BlueStacks will delete the program and update you when it’s complete. The other BlueStacks files may still be installed on your device, but you can follow these steps again to remove them.
macOS
To uninstall BlueStacks:
- Open BlueStacks and click on BlueStacks in the menu bar. From the drop-down menu, click Uninstall BlueStacks.
- Confirm you want to uninstall BlueStacks. Click on Yes to proceed.

BlueStacks and its files will be removed from your Mac.
FAQ: Common questions about BlueStacks
Is BlueStacks a Chinese company?
No, BlueStacks is a U.S.-based company founded in Palo Alto. Its partnerships include various American companies, such as, for example, the semiconductor and hardware manufacturer AMD.
Is BlueStacks legal?
Android emulators are legal to use, and BlueStacks doesn’t circumvent device protections or modify copyrighted content. The legality of running specific apps in BlueStacks depends on their terms of service.
How do I maximize safety on BlueStacks?
Treat BlueStacks the same way you treat your Android phone, and follow the best security practices. Download the installer from the official website, install apps from trusted sources only, and review permissions before granting access. Keeping both BlueStacks and your operating system updated also helps reduce risk.
Does BlueStacks contain malware or viruses?
The official BlueStacks installer does not contain any type of malware, including viruses. However, versions downloaded from unofficial download sites can include harmful code, bundled adware, or unwanted programs, so downloading from the correct source is essential.
Some antivirus programs may still flag the legitimate version of BlueStacks with a warning. This usually happens because emulators create virtual environments, inject processes, or adjust system settings in ways that resemble suspicious behavior. These alerts are typically false positives, not evidence of malicious code.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN